5 common health conditions men don’t like to talk about
Some of the most common conditions affecting men carry a social stigma but are highly treatable. Learn about the top 5 health conditions men should be talking about.
Men should not let fear or embarrassment prevent them from discussing their health concerns with each other or their health care provider.
Men’s health risks can increase with age. Learning early warning signs of serious health conditions is vital. Information about health issues can even be lifesaving. Men sometimes don't talk about their health. They keep quiet at times because of culture, attitude, fear, or pride.
Here is information about 5 health conditions.
Screenings are key for prostate cancer
One in 8 men will face a prostate cancer diagnosis, and the majority are 65 and older. Men 50 and older should be checked for prostate cancer. Men with prostate cancer in their family should talk to their doctor and start getting screened at 45.
Some men may feel uneasy about health screenings, such as digital rectal exams. Regular exams are important. Prostate cancer often does not have symptoms in its earliest stages. Some signs of prostate cancer may include problems urinating or blood in urine.
Colorectal cancer affects men and women
Colorectal cancer, or colon cancer, is one of the most treatable cancers when detected and treated early. If you are between 45 and 49, talk with your doctor or care team to request a FIT kit. Colon cancer screening is recommended starting at age 45 for people at average risk; earlier if you’re high risk.
Most cases of colon cancer come from precancerous polyps that don’t cause symptoms for a long time. People with a family history of colon cancer are at increased risk. Taking steps to understand your unique risk can help with early detection.
Testicular cancer is most common in young men
The most common cancer in men 20 to 34 years old is testicular cancer. This cancer can also affect children and older men as well.
Unfortunately, social stigma can be a barrier to men discussing testicular cancer. Self-examination is important. The first symptoms can include a lump or swelling in the scrotum that may or may not be painful. Other symptoms may also be present, such as a feeling of heaviness in the lower abdomen.
When found early and before it has spread, testicular cancer is highly treatable.
ED may be a warning sign
Erectile dysfunction, or ED, describes difficulty achieving or keeping an erection. Some men may not be comfortable discussing ED even though it is often treatable. ED is often a sign of other health issues, including heart disease or diabetes.
ED is especially prevalent in men over 40 and those with diabetes. If untreated, ED can cause a loss of intimacy in a relationship. ED can also contribute to emotional distress.
Consult your doctor if there are concerns about ED.
Men and breast cancer
Men can develop breast cancer just like women. Men may feel embarrassed discussing a lump or swelling on the breast. Men with a family history of breast cancer, such as a mother or sister with the disease, are at increased risk.
Common symptoms of breast cancer include a lump or swelling under the arm, a rash around the nipple, nipple discharge, or pain in the nipple area. Men who have any of these symptoms should consult their doctor.
If left untreated, breast cancer can spread to other parts of the body.
Men should not let fear or embarrassment prevent them from discussing their health concerns.
Regular health maintenance and checkups are important. Identifying problems early can prevent them from developing into more serious problems.
Learn more about preventive care at Kaiser Permanente.
-
Social Share
- Share 5 Common Health Conditions Men Don’t Like To Talk About on Pinterest
- Share 5 Common Health Conditions Men Don’t Like To Talk About on LinkedIn
- Share 5 Common Health Conditions Men Don’t Like To Talk About on Twitter
- Share 5 Common Health Conditions Men Don’t Like To Talk About on Facebook
- Print 5 Common Health Conditions Men Don’t Like To Talk About
- Email 5 Common Health Conditions Men Don’t Like To Talk About
March 27, 2025
Living proof: Colon cancer highly treatable if caught early
There is an alarming rise in colon cancer rates among younger adults. Cynthia …

February 26, 2025
Colon cancer: Do you need to be screened?
If you’re age 45 or older, getting checked regularly for colorectal cancer …

February 26, 2025
Spring into a better night’s sleep
A Kaiser Permanente sleep expert shares tips for decreasing the impact …

February 20, 2025
Kaiser Permanente joins Food Is Medicine Colorado coalition
As an inaugural member, Kaiser Permanente will help lead health care’s …

February 14, 2025
A fulfilling life on the other side of ovarian cancer
As a wife and a mother, Autumn Gray was determined to beat cancer to be …

February 12, 2025
Back on track after a rare cancer diagnosis
After facing sarcoma at age 18, drag-racing champion Cooper Chun needed …

January 24, 2025
Is one drink a day OK? Here’s what to consider
NPR

January 13, 2025
How to prevent cervical cancer
Cervical cancer is highly preventable. HPV vaccination and regular screenings …

December 26, 2024
How telehealth can make life easier for people with cancer
Virtual care connects cancer patients like Rob Tufel to a wide range of …

November 26, 2024
Personalize your care with a family health history
Talk with your family members about their medical conditions. What you …

November 26, 2024
How to reduce your risk of stroke
A Kaiser Permanente doctor and researcher shares the simple changes you …

November 22, 2024
Breast cancer survivor encourages early testing
Tasha Champion shares how early testing by her oncologist at Kaiser Permanente …

November 18, 2024
The power of early detection and proactive men’s health
A father's determination to stay healthy for his 3 children led him to …

October 1, 2024
Screening for breast cancer: Mammogram guidelines
A Kaiser Permanente radiologist answers commonly asked questions.

September 20, 2024
Ovarian cancer journey confirmed nursing student's calling
Miriam Gutierrez was diagnosed with late-stage ovarian cancer at age 31. …
September 18, 2024
More than 100 ‘Top Docs’ recognized in Washington state
Kaiser Permanente celebrates doctors and nurse practitioners recognized …

September 18, 2024
Cancer rates are rising in younger age groups
‘Connect’ with research to help understand more about the increase of certain …

September 17, 2024
Playing on after 2 decades of cancer care
With the support of his health care team and nurse navigator, musician …

August 29, 2024
After Stage 4 ovarian cancer, she’s still going strong
Donna Budway received prompt surgery followed by chemotherapy. She credits …

August 26, 2024
Katie's ride: Motorcycle rally a surprise for patient
Kaiser Permanente in San Diego helped plan a special send-off for Katie …
August 15, 2024
Back home one day after heart surgery
Ed Dalmasso needed an aortic valve replacement. His care team provided …

August 6, 2024
For a father with prostate cancer, knowledge is power
Harold Newman had advanced prostate cancer. Genetic testing helped expand …

August 1, 2024
Early prostate cancer detection helps one patient fight back
After a successful treatment, Luke Klein is giving back as a mentor who …

July 10, 2024
Grant to help make school lunches healthier for kids
Chef Ann Foundation will use $275,000 grant for Colorado program to convert …

June 28, 2024
Operation Splash makes a splash for safe summer fun
Kaiser Permanente is making waves this summer, ensuring that communities …

June 17, 2024
A culture of caring eases a cancer journey
Exceptional, personalized radiation oncology care helped Maura Craig treat …

June 13, 2024
Conquered 2 cancers while climbing mountains
Chris Hogan faced kidney cancer and prostate cancer at the same time. He …

June 3, 2024
A call to ‘Connect’ for cancer prevention research
Participate in a study to help uncover the causes of cancer and how to …

May 31, 2024
Stage 4 lung cancer: A story of hope
A young father is enjoying “bonus time” with his kids thanks to new targeted …

May 21, 2024
Surviving stage 4 lung cancer with immunotherapy treatment
Patients like Carol Pitman are living longer thanks to advances in lung …

May 7, 2024
Making cancer care more convenient in Southern California
Kaiser Permanente has opened a new Radiation Oncology Center at the Bellflower …
April 23, 2024
We’re rising up to help prevent falls
Kaiser Permanente is committed to finding ways to help reduce falls in …

April 9, 2024
Denver Fire Department annual blood work screenings triple
It’s easy to put off recommended health screenings, and sometimes even …

April 1, 2024
Lynch syndrome: Managing the risk of hereditary colon cancer
Lynch syndrome is a gene mutation that increases colon cancer risk. Learn …

March 20, 2024
Life after cancer: Surviving and thriving
A healthy life after cancer is possible. Learn how Kaiser Permanente helps …

March 14, 2024
Healthy kidneys support overall good health
Kaiser Permanente excels in preventing, detecting, and treating kidney …

March 6, 2024
Joining a national effort to test new ways to find cancer
As part of the Cancer Screening Research Network, our researchers will …

March 6, 2024
Colon cancer screening: She’s glad she didn’t wait
A timely preventive test reveals Rebecca Kucera has cancer. Swift treatment …

March 5, 2024
Researchers look for ways to find pancreatic cancer early
Early detection of the disease, before it becomes advanced, will increase …

February 21, 2024
Recovering at home after a double mastectomy
Innovative surgical recovery program helps breast cancer patients safely …

January 31, 2024
Prioritizing policies for health and well-being in Colorado
CityHealth’s 2023 Annual Policy Assessment awards cities for their policies …

January 24, 2024
A full-circle journey for one cancer survivor
Grateful for compassionate and successful Hodgkin lymphoma treatment at …

January 10, 2024
‘You don’t know unless you ask them’
Kaiser Permanente’s Patient Advisory Councils help us create exceptional …
December 20, 2023
Research transforms care for people with multiple sclerosis
Our researchers are leading the way to more effective, affordable, and …

December 13, 2023
Nurse navigators guide patients from diagnosis to treatment
An unexpected cancer diagnosis left Jennifer Martin unsure of the next …

December 12, 2023
Hundreds attend first Food Is Medicine Summit
Attendees look at ways to get healthy food to people who don’t have enough …

December 6, 2023
Leading research with gratitude
Learn how you can participate in a study to uncover what causes cancer …

December 1, 2023
Surviving — and thriving — after cancer
From diagnosis to recovery, David Parsons, MD, shares how screening, treatment, …

October 25, 2023
Breast cancer during pregnancy: Caring for mom and baby
A team of specialists treats an expecting mother’s cancer while keeping …

October 23, 2023
A renewed sense of purpose after surviving breast cancer
Joy Short, a Kaiser Permanente member and employee, turned her breast cancer …

October 11, 2023
Early breast cancer detection improves quality of life
For 75-year-old Peggy Dickston, a surprise diagnosis was caught early thanks …

September 20, 2023
Healing after a heart attack
For years, serious heart attacks meant hours of weekly appointments. Now, …

September 13, 2023
Transforming the medical record
Kaiser Permanente’s adoption of disruptive technology in the 1970s sparked …

August 29, 2023
Preventing overdoses starts with education
Risk factors are not always associated with addiction or substance abuse. …

August 17, 2023
Beyond clinic walls: Research supporting healthy communities
Stories in the Department of Research & Evaluation 2022 Annual Report demonstrat …

August 17, 2023
Cancer research: The role of immunotherapy
Research and clinical trials play a vital role in advancing cancer treatment …

August 16, 2023
Cervical cancer screening: Exploring the at-home HPV test
Kaiser Permanente is at the forefront of cervical cancer research. Find …

August 14, 2023
Tips for ensuring a safe and healthy college experience
Students should study up on their care options to ace their school experience. …

August 14, 2023
Marla’s story: Surviving acute promyelocytic leukemia
After a diagnosis for a rare type of blood cancer, Marla Marriott got high-quali …

August 4, 2023
Eating well and adopting healthy habits helps prevent cancer
Learn how lifestyle medicine is part of cancer care at Kaiser Permanente.

July 27, 2023
Courageously facing hereditary breast cancer
Fay Gordon's breast cancer was caught in the early stages thanks to genetic …
July 26, 2023
Can you get chemotherapy while pregnant?
Chemotherapy can be an option during pregnancy. Find out how Kaiser Permanente …

July 21, 2023
Thankful for every day after HPV-related cancer diagnosis
Michael West shares his incredible journey from diagnosis to treatment …

July 14, 2023
Breast reconstruction surgery after cancer
A Kaiser Permanente plastic surgeon explains breast reconstruction options …

July 10, 2023
Beating colon cancer together: Miguel and Paula’s story
After they were both diagnosed with colon cancer, Miguel and Paula fought …

June 30, 2023
Men's mental well-being is a priority
Unique challenges and societal pressures can impact men’s emotional well-being.

June 30, 2023
Doctors' top tips to manage prostate cancer risk factors
Regardless of your age, race, or family history, you can take steps to …

June 30, 2023
Lung cancer survivor received ‘pioneering’ care
Doctor and mother of 3 Susan Brim received top-notch care after her lung …

June 27, 2023
Men: It’s time to prioritize preventive care
It’s important to be proactive about your health by scheduling regular …
June 27, 2023
Comforting, personalized care for a kiddo with cancer
Carter Shaver from Portland, Oregon, shares his optimistic smile after …

June 22, 2023
Higher survival rates for our patients with colon cancer
A new study compares Kaiser Permanente members in Southern California to …

June 15, 2023
Stay safe while having fun in the sun
Tips for preventing sunburn and decreasing the risk of skin cancer.

June 14, 2023
Living with stage 4 breast cancer
Thanks to personalized care from a team of skilled doctors, Christina McAmis …

May 30, 2023
The healing power of shared cancer experience
Peer mentoring program matches new cancer patients with others who’ve gone …

April 25, 2023
Hannah Peters, MD, provides essential care to ‘Rosies’
When thousands of women industrial workers, often called “Rosies,” joined …

April 14, 2023
The importance of screening for gestational diabetes
Gestational diabetes poses a significant risk to women of color, particularly …

April 7, 2023
Increasing access to health care
Kaiser Permanente launches new mobile health vehicle on Oahu.

March 17, 2023
A call to 'Connect' for cancer research
A new study invites participants in Oregon to help uncover what causes …

March 14, 2023
Colorectal cancer on the rise among younger adults
Learn why early screening is crucial for prevention and treatment.

February 28, 2023
What you need to know about COPD
Almost 16 million people in the United States have chronic obstructive …

February 27, 2023
Teaching flu a lesson
School-based flu vaccination clinics made it safe and convenient for students …

February 15, 2023
A new chapter for male patient with breast cancer
A multidisciplinary care team acted fast to help save the life of a Kaiser …

January 27, 2023
Timely flu vaccinations at community events
Proactive flu prevention outreach helped community members in Downey, California …

January 13, 2023
Making dreams come true
Member achieves bucket list goal of helping to build a Rose Parade float, …
December 22, 2022
Denver earns an overall gold medal
CityHealth recognizes Denver for its leadership in supporting policies …
December 21, 2022
From cancer patient to cancer colleague
A Kaiser Permanente member’s cancer journey inspires her to join the team …

November 14, 2022
It’s time to rethink health care quality measurement
To meaningfully improve health equity, we must shift our focus to outcomes …
November 11, 2022
Our integrated care model
We’re different than other health plans, and that’s how we think health …

August 17, 2022
Cancer clinical trials: Can they help find a cure?
These important research studies aim to help patients live longer, better …

May 5, 2022
Research study will inform the future of cancer prevention
Connect for Cancer Prevention Study’s goal to recruit 200,000 participants …

April 20, 2022
The perfect match: Living kidney donation saves LAPD officer
Bobbie Norman is grateful for 15 years of health after his wife — a fellow …

July 30, 2021
Pairing doctors with your devices for improved health
Wellness and fitness-tracking devices can help doctors and patients coordinate …

June 8, 2021
Cancer patients and physicians embrace telehealth
Video visits and virtual collaboration speed cancer care transformation …
April 5, 2021
Weight linked to risk of second cancer after breast cancer
Kaiser Permanente study has important public health implications given …

February 22, 2021
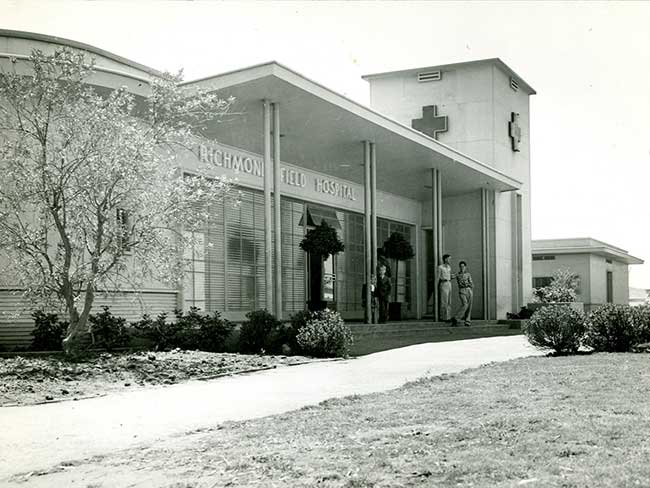
The Permanente Richmond Field Hospital
Forlorn and all but forgotten, it played a proud role during the World …
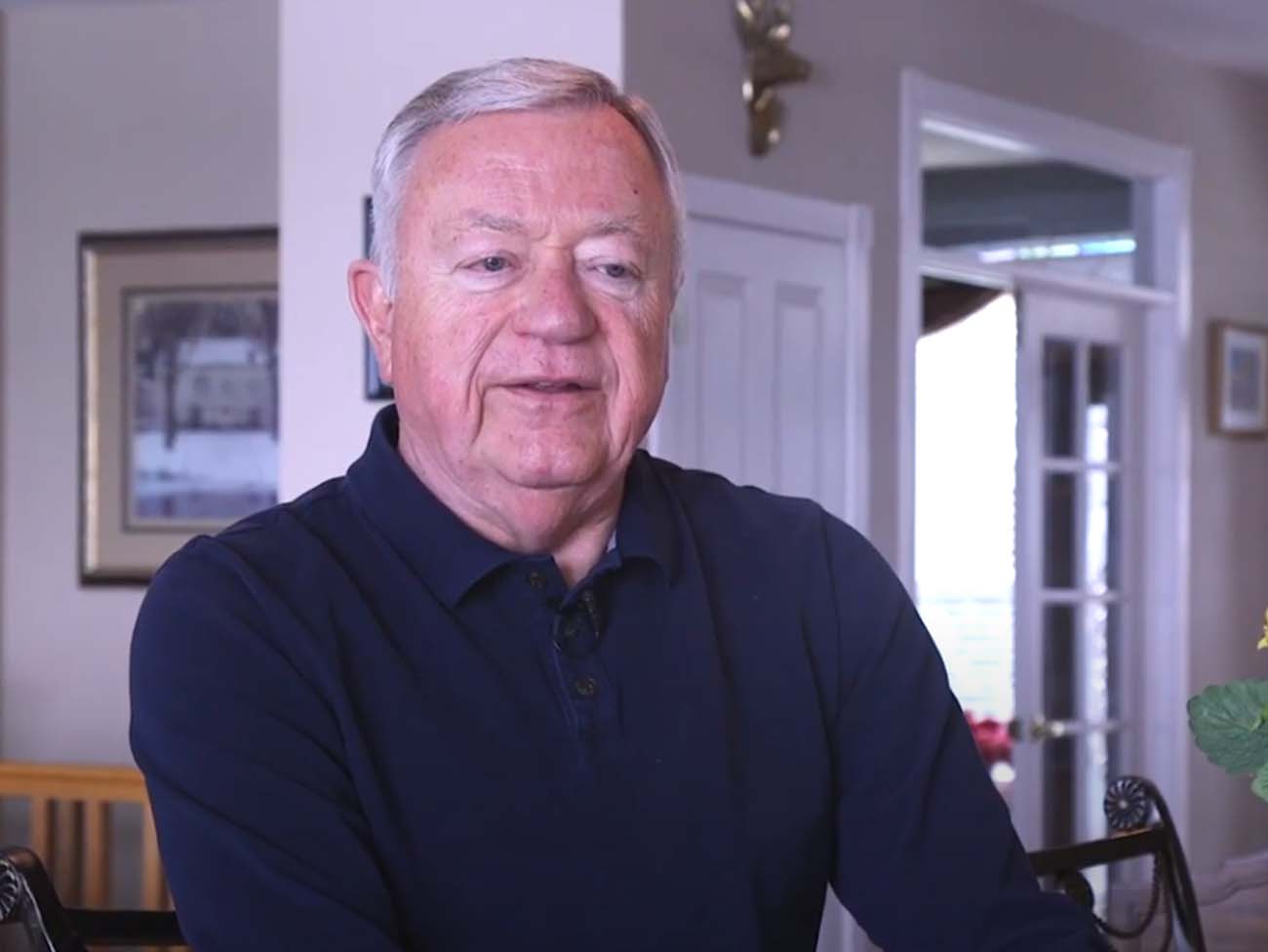

July 21, 2020
Diagnostic and preventive care is in our DNA
A routine screening helped detect Bill Walsh’s cancer before it became …

January 21, 2020
Destination health: Stopping cancer before it starts
Kaiser Permanente is creating more healthy life years with a combined focus …
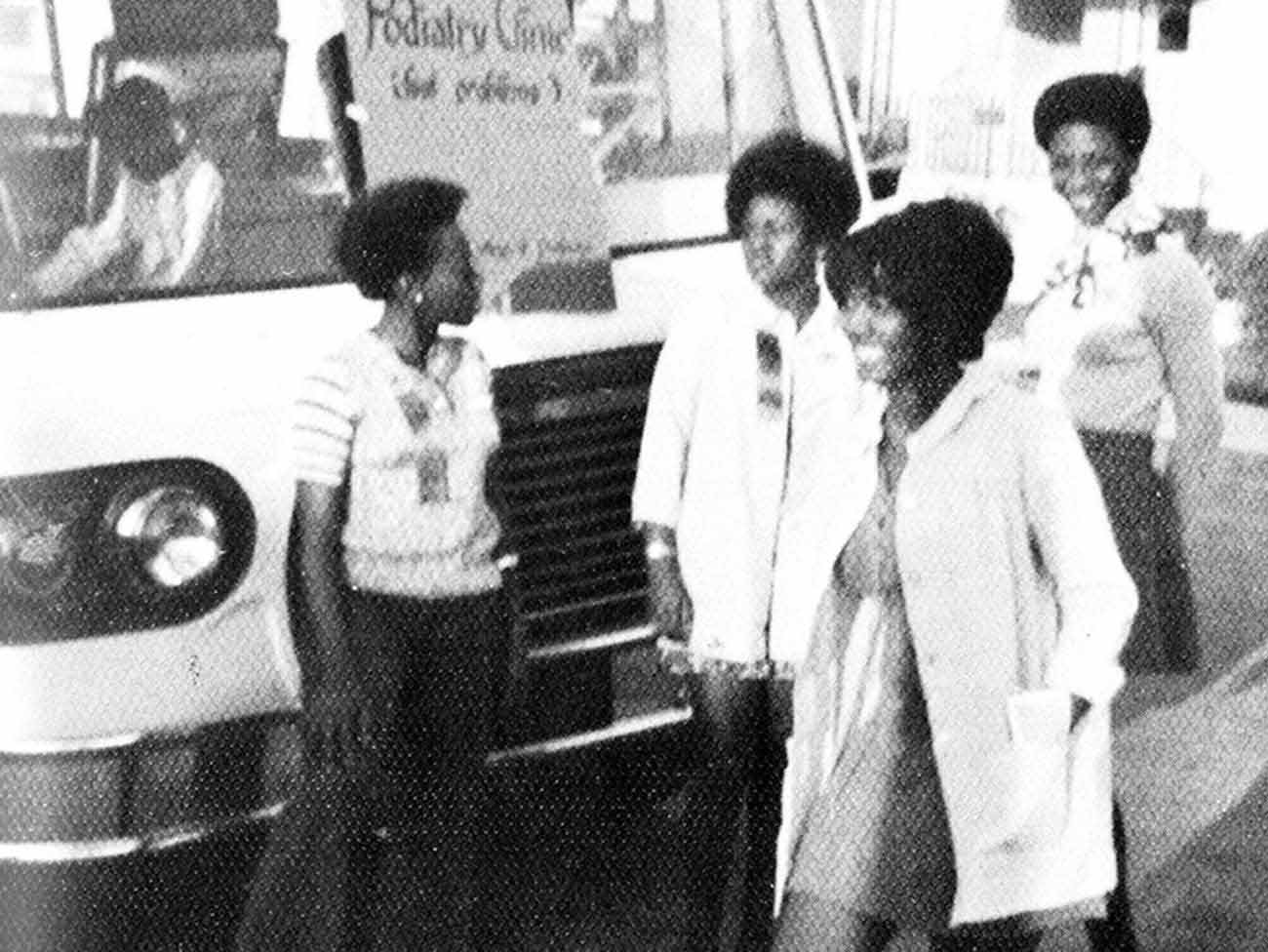

February 5, 2019
Mobile clinics: 'Health on wheels'
Kaiser Permanente mobile health vehicles brought care to people, closing …

August 15, 2017
Sidney R. Garfield, MD, on medical care as a right
Hear Kaiser Permanente’s physician co-founder talk about what he learned …
March 1, 2017
Screening for better health: Medical care as a right
When industrial workers joined the health plan, an integrated battery of …